get to know the different types
of EV charging!


Electric vehicles are the key technology for reducing C02 emissions in the transportation sector, which contributes approximately one-sixth of global emissions. The sustained growth of EV markets worldwide relies heavily on the implementation of ambitious policies aimed at promoting their adoption and proliferation.
Over the past few years, we have witnessed remarkable growth in sales, accompanied by improved range, wider model options and increased performance.
Currently, home charging meets the majority of charging demand for electric vehicles. However, there is a growing necessity for publicly accessible charging infrastructure to match the convenience and accessibility of traditional vehicle refueling stations. Looking ahead to 2030, the Net Zero Scenario (IEA) anticipates the installation of 17 million publicly available charging stations worldwide.
But, how many types of EV Chargers there are?
Electric Vehicles charging has three levels, in the US, based on charging voltage. The higher the voltage, the faster the charge. Depending on battery size, charging an EV battery to 80-100% capacity can take from 30 minutes to 12 hours.
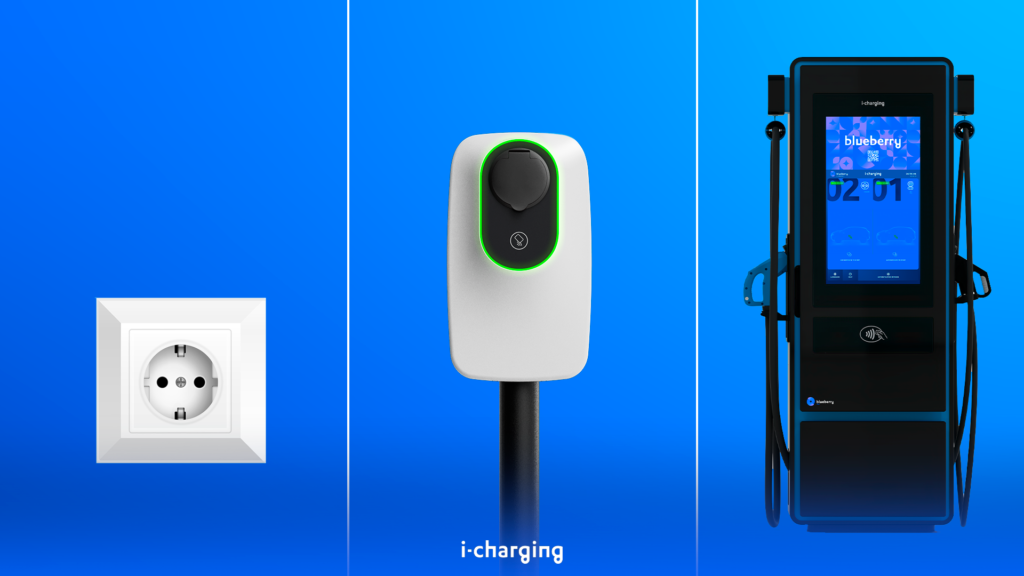
Level 1
At the base of the EV charging hierarchy lies Level 1 charging, referred to as “trickle charging.” Utilizing a standard household outlet (120 volts), Level 1 charging provides a modest 3-5 miles of range per hour, making it ideal for overnight charging routines. Although Level 1 charging may be slow, it is adequate for daily commuting and short rides, offering roughly 50 miles of range with a full night’s charge.
Level 2
Level 2 charging offers increased versatility and efficiency. Using a 240-volt outlet similar to those used for household appliances like dryers or stoves, Level 2 chargers provide 12-80 miles of range per hour, making them suitable for both residential and commercial settings. Even though installation may require additional investment, specialized splitters offer cost-effective alternatives for households lacking dedicated 240-volt outlets.
Level 3
For those in need of rapid charging, Level 3, also known as DC Fast Charging, delivers unparalleled speed and convenience. With 480 volts, Level 3 chargers can fill an EV’s battery to 80% capacity in as little as 30 minutes, offering between 3-15 miles per minute. Typically found at dedicated fast-charging networks, Level 3 stations are similar to traditional gas stations, providing a seamless solution for long-distance travel.
In Europe, there are two types of charging: AC and DC as in US,
however there are four modes of charging an EV:
Mode 1 – Standard socket outlet – domestic installation
Mode 2 – Standard socket outlet with an AC EV supply equipment– domestic
Mode 3 – AC EV equipment permanently connected to an AC supply network
Mode 4 – DC EV Supply equipment
AC charging is slow when compared to DC charging, that could be Fast to Ultra-Fast Charging, mode 4.
Slow chargers can be single-phase, or three-phase and the current can vary: 16 A or 32 A, resulting in power ranges from 3 kVA to 22 kVA. Charging and EV with a slow charger has a duration of hours, when compared to Fast and Ultra-Fast chargers that charge in minutes. In these cases, power is typically 50 kW for fast- chargers, and more than 150 kW for ultra-fast charging.
In conclusion, there are three levels of charging in the US and four modes of charging in Europe and there are two types of EV chargers, AC and DC, that offer distinct advantages and cater to varying needs and preferences. As the EV landscape continues to evolve, investing in charging infrastructure is crucial for realizing the full potential of electric mobility and ushering in a greener, more sustainable future.